Long story short: Road tax in India is a key aspect of vehicle ownership, imposed by states and union territories to support road infrastructure maintenance and development. The two-wheeler rates vary by state and depend on engine capacity, vehicle age, and weight. This article offers a clear overview of state-wise road tax for two-wheelers and addresses common questions and misconceptions about road tax.
Key Takeaways
- Road tax in India is a mandatory state and union territory levy on vehicles, including motorcycles, based on engine capacity, seating, age, and weight.
- State-wise road tax helps generate local revenue for infrastructure development. States can set tax rates based on their economic and infrastructure needs.
- Varying tax rates across states create confusion for vehicle owners. Economic disparities arise as higher-tax states may face lower vehicle sales.
- The state-wise road tax system benefits states like Punjab and Haryana by allowing them to generate localized revenue, which can be used for infrastructure development and maintenance.
- In states like West Bengal and Odisha, road tax rates are determined based on engine capacity and vehicle cost, highlighting the diverse taxation structures in different regions.
How Two wheeler road tax is levied in India?
Road tax is a mandatory tax levied by state and union territories in India on vehicles, including motorcycles, based on various factors such as engine capacity, seating capacity, vehicle age, and weight. The tax rates and calculation methods vary significantly across different states and cities.
Pros of State Wise Road Tax
Localized Revenue Generation
State-wise road taxes allow individual states to generate revenue that can be directly used to maintain and develop local road infrastructure. This ensures that the funds are utilized where they are most needed.
Tailored Tax Rates
States can set tax rates based on their economic conditions and infrastructure needs. This flexibility allows for a more customized approach to taxation.
Encourages Local Governance
State-wise taxation empowers local governments to make decisions that best suit their residents, promoting a sense of autonomy and regional governance.
Cons of State Wise Road Tax
Complexity and Confusion
Different tax rates and regulations across states can confuse vehicle owners, especially those who relocate frequently. This complexity can lead to non-compliance and administrative challenges.
Economic Disparities
Varying tax rates can lead to economic disparities between states. States with higher taxes may see a decline in vehicle sales, impacting their local economies.
Administrative Burden
Managing and enforcing state-wise taxes requires significant administrative resources. This can be cumbersome and inefficient compared to a centralized system.
Pros of Centralized Road Tax (Not applicable in India)
Simplified Compliance
A single, unified road tax rate across the country would eliminate the complexity and confusion caused by different state tax rates. This would make it easier for vehicle owners to understand and comply with tax regulations.
Economic Integration
A centralized tax system would promote economic integration and mobility, especially for the dynamic and mobile workforce of 21st-century India. It would create a level playing field for all states and union territories.
Reduced Administrative Costs
Centralized taxation would streamline the administrative process, reducing the burden on state governments and potentially lowering the overall cost of tax collection.
Cons of Centralized Road Tax (Not applicable in India)
Loss of State Revenue
States may lose a significant source of revenue, which could impact their ability to maintain and develop local infrastructure and lead to dependency on central government allocations.
One-Size-Fits-All Approach
A uniform tax rate may not account for different states’ diverse economic conditions and infrastructure needs. This could lead to inefficiencies and inequities in resource allocation.
Implementation Challenges
Transitioning to a centralized tax system would require careful planning, coordination, and consensus-building among the central and state governments. This could be a complex and time-consuming process.
State Wise Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers in India
Road Tax for Two-Wheelers in Southern States in India
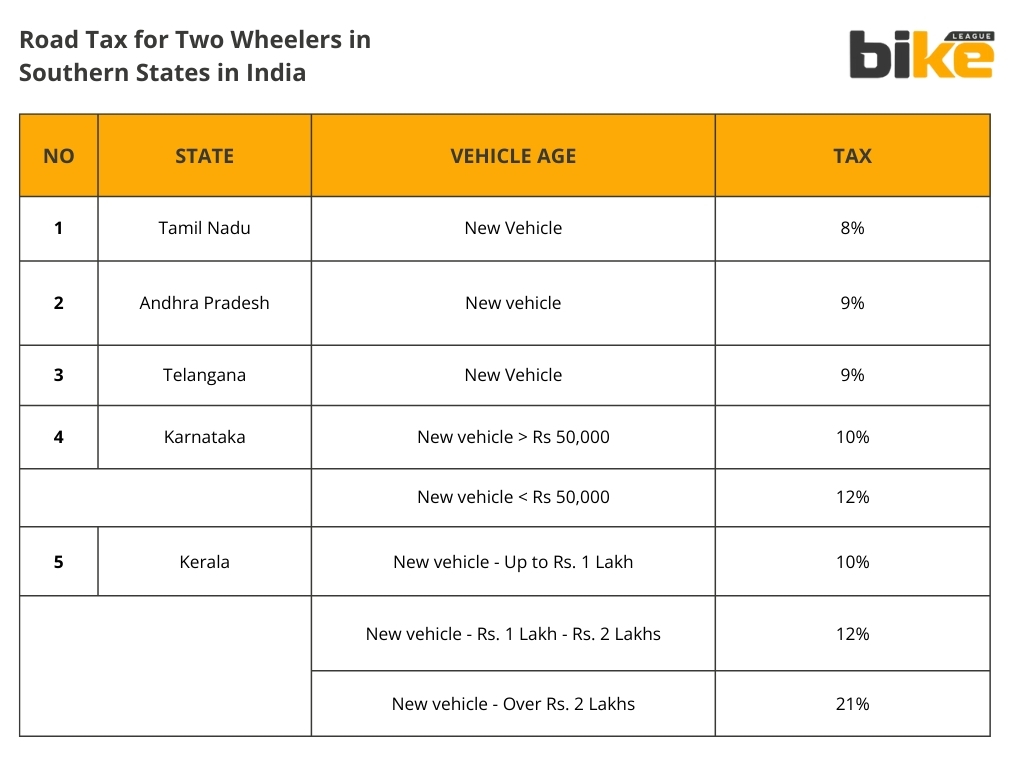
1. Andhra Pradesh Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- New Vehicle: 9% of the total cost of the vehicle.
- Age-based taxation: Up to 2 years: 8%
- 2 – 3 years: 7%
- 3 – 4 years: 6%
- 4 – 5 years: 5%
- 5 – 6 years: 4%
- 6 – 7 years: 3.5%
- 7 – 8 years: 3%
- 8 – 9 years: 2.5%
- 9 – 10 years: 2%
- 10 – 11 years: 1.5%
- Greater than 11 years: 1%
2. Karnataka Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- New vehicle costing less than Rs. 50,000: 10%.
- New vehicle costing more than Rs. 50,000: 12%.
- Vehicles no more than 5 years old: 73% to 93%.
- Vehicles between 5-10 years old: 49% to 69%.
- Vehicles between 10-15 years old: 45% to 25%.
- Electric Vehicles: 4%.
3. Kerala Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- New Motorcycles up to Rs. 1 Lakh: 10% of the purchase value.
- Motorcycles between Rs. 1 Lakh and Rs. 2 Lakhs: 12% of the purchase value.
- Motorcycles over Rs. 2 Lakhs: 21% of the purchase value.
4. Tamil Nadu Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- New two-wheelers: 8% of the total cost of the vehicle.
- Age-based taxation: 0-1 year: 7.75%, 1-2 years: 7.5%, 2-3 years: 7.25%, 3-4 years: 7%, 4-5 years: 6.75%, 5-6 years: 6.5%, 6-7 years: 6.25%, 7-8 years: 6%, 8-9 years: 5.75%, 9-10 years: 5.5%, 10-11 years: 5.25%, 11-12 years: 5%
5. Telangana Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- New Vehicle: 9% of the total cost of the vehicle.
- Age-based taxation: Up to 2 years: 8%, 2 – 3 years: 7%, 3 – 4 years: 6%, 4 – 5 years: 5%, 5 – 6 years: 4%, 6 – 7 years: 3.5%, 7 – 8 years: 3%, 8 – 9 years: 2.5%, 9 – 10 years: 2%, 10 – 11 years: 1.5%, Greater than 11 years: 1%
Road Tax for Two wheelers in Northern states in India
1. Haryana Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- For vehicles priced up to Rs. 75,000, the tax rate is 4% of the vehicle’s cost.
- For vehicles priced above Rs. 75,000 and up to Rs. 2 lakhs, the tax rate is 6% of the vehicle’s cost.
- For vehicles priced above Rs. 2 lakhs, the tax rate is 8% of the vehicle’s cost.
2. Himachal Pradesh Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Up to Rs. 1 Lakh: The road tax is 6% of the vehicle’s price. This category includes most entry-level and mid-range bikes and scooters, making them relatively affordable in terms of tax.
- Over Rs. 1 Lakh: For vehicles costing more than Rs. 1 lakh, the tax rate is 7% of the price of the vehicle. This range typically covers higher-end bikes and premium scooters.
Additional Tax Information
General Road Tax Rate: Besides the value-based rates, the general road tax rate is 8% for vehicles costing up to Rs. 15 lakhs. For vehicles costing more than Rs. 15 lakhs, the applicable tax slab is 9% of the vehicle cost.
3. Rajasthan Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Up to 200 cc: 8% of the cost of the vehicle.
- more than 200 cc and up to 500 cc: 13% of the cost of the vehicle.
- more than 500 cc: 15% of the cost of the vehicle.
4. Punjab Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
Two types of tax rates are used; one before any amendment was made to The Motor Vehicles Taxation Act 1924 and another after its amendment in 1993.
Road Tax Based on Vehicle Age and Weight (Before the Amendment)
- Under 3 years of age: Rs. 120 for bikes up to 95 kg, Rs. 400 for bikes over 95 kg.
- Between 3 and 6 years: Rs. 90 for bikes up to 95 kg, Rs. 300 for bikes over 95 kg.
- Between 6 and 9 years: Rs. 60 for bikes up to 95 kg, Rs. 200 for bikes over 95 kg.
- More than 9 years: Rs. 30 for bikes up to 95 kg, Rs. 100 for bikes over 95 kg.
Road Tax Based on Engine Capacity (After the Amendment)
For bikes registered after the amendment of the act, the road tax is calculated based on the engine capacity:
- Engine power up to 50cc: 1.5% of the bike’s cost.
- Engine power of more than 50cc: 3% of the bike’s cost.
This differentiation encourages the use of smaller, more fuel-efficient bikes by imposing a lower tax rate on them.
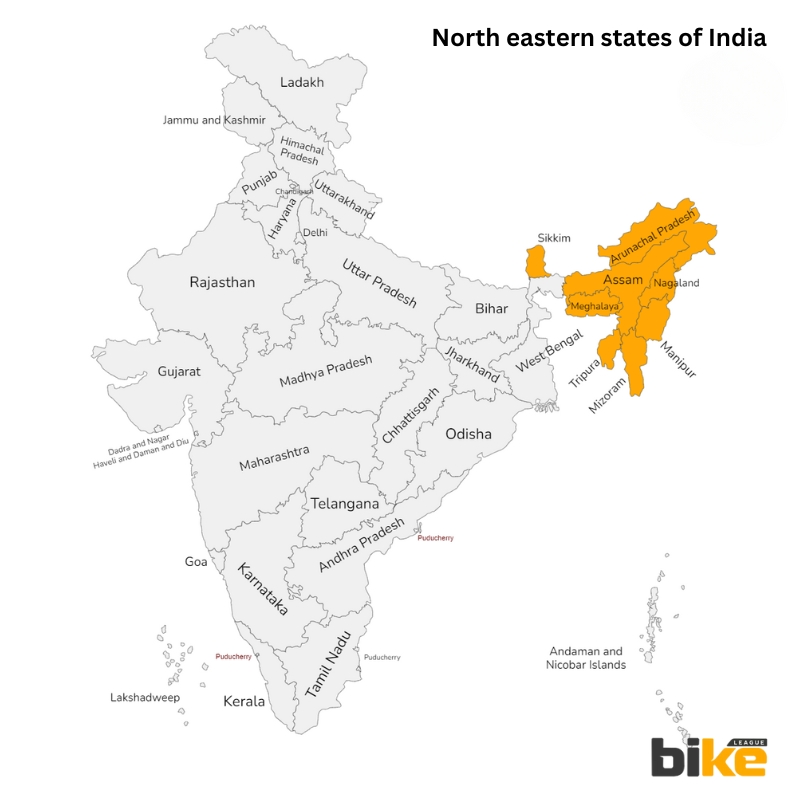
Road Tax for Two wheelers in Northern Eastern states in India
1. Assam Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Less than 65 kg: Rs. 1,500 for 15 years, and Rs. 500 for every subsequent 5 years.
- 65 kg to 90 kg: Rs. 2,500 for 15 years, and Rs. 700 for every subsequent 5 years.
- 90 kg to 135 kg: Rs. 3,500 for 15 years, and Rs. 1,000 for every subsequent 5 years.
- More than 135 kg: Rs. 4,000 for 15 years, and Rs. 1,000 for every subsequent 5 years.
- Additionally, two-wheelers with sidecars incur an extra charge of Rs. 1,000.
- For vehicles transferred from other states, a depreciation of 7% per annum is applied.
2-4. Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Less than 65 kg: ₹1,100 for 10 years, and ₹310 for every subsequent 5 years.
- 65 kg to 90 kg: ₹1,800 for 10 years, and ₹470 for every subsequent 5 years.
- 90 kg to 135 kg: ₹2,500 for 10 years, and ₹630 for every subsequent 5 years.
- More than 135 kg: ₹2,990 for 10 years.
5. Mizoram Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
Mizoram calculates the two-wheeler road tax based on the vehicle’s engine capacity. The rates are:
- Motorcycles: 12% of the vehicle’s price.
Specific vehicles are exempted from paying road tax in Mizoram, including two-wheelers with engine capacity not exceeding 50 cc, electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and CNG/LPG-fueled vehicles.
6. Nagaland Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
One-Time Tax Payment
In Nagaland, the road tax for two-wheelers is typically a one-time payment covering 15 years. Once the tax is paid, the vehicle owner does not need to worry about annual fees for the next 15 years.
Tax Rate
The road tax rate for two-wheelers in Nagaland is 5% of the vehicle’s cost, calculated based on the vehicle’s ex-showroom price. This straightforward calculation method ensures that the tax amount is proportional to the vehicle’s value.
Exemptions
In Nagaland, two-wheeled electric vehicles are exempt from road tax. The state is implementing this exemption as part of its initiative to promote environmentally friendly transportation options.
7. Tripura Road Tax Rates for Two-Wheelers
- Geared personal-use two-wheelers priced above Rs. 1 lakh: Rs. 2,650 as a one-time payment for the initial 15 years, and Rs. 1,100 for every subsequent 5 years.
8. Sikkim Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Under 80 cc engine capacity: The road tax is Rs 100. This category includes smaller bikes and scooters with lower engine capacities, making them more affordable in terms of tax.
- Between 80 and 170 cc engine capacity: The tax rate for this category is Rs 200. This range typically covers most commuter bikes.
- Between 170 and 250 cc engine capacity: The tax is Rs 300 on bikes with engine capacities in this range. These are often higher-performance bikes used for both commuting and leisure.
- Over 250 cc engine capacity: The highest tax rate of Rs 400 applies to bikes with engines exceeding 250 cc, usually premium or sports bikes.
Additional Tax Information
General Road Tax Rate:
In addition to the engine capacity-based rates, there is a general road tax rate of 8% of the vehicle’s cost, which is applied to the two-wheeler’s ex-showroom price.
Registration Fee:
A standard fee of Rs 300 applies to all two-wheelers.
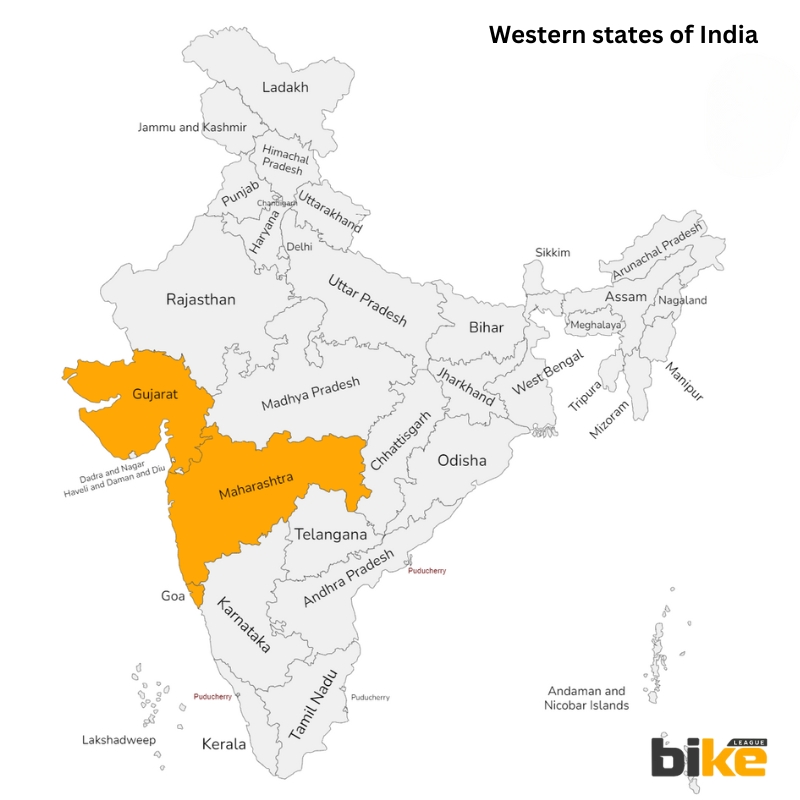
Road Tax for Two wheelers in Western states in India
1. Goa Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Vehicles costing not more than Rs 1.5 Lakhs: 9%
- Vehicles costing more than Rs 1.5 Lakhs but less than Rs 3 Lakhs: 12%
- Vehicles costing more than Rs 3 Lakhs: 15%
2. Gujarat Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- New vehicles and those less than 8 years old: 6% of the cost of the vehicle.
- Vehicles between 8 and 15 years old: 15% of the cost of the vehicle.
- Vehicles older than 15 years: 1% of the cost of the vehicle or 100 INR, whichever is higher.
3. Maharashtra Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Motorcycles with engine capacity below 99 cc: 10% (minimum of Rs. 1,500)
- Motorcycles with engine capacity between 99 and 299 cc: 11% (minimum of Rs. 1,500)
- Motorcycles with engine capacity above 299 cc: 12% (minimum of Rs. 1,500)
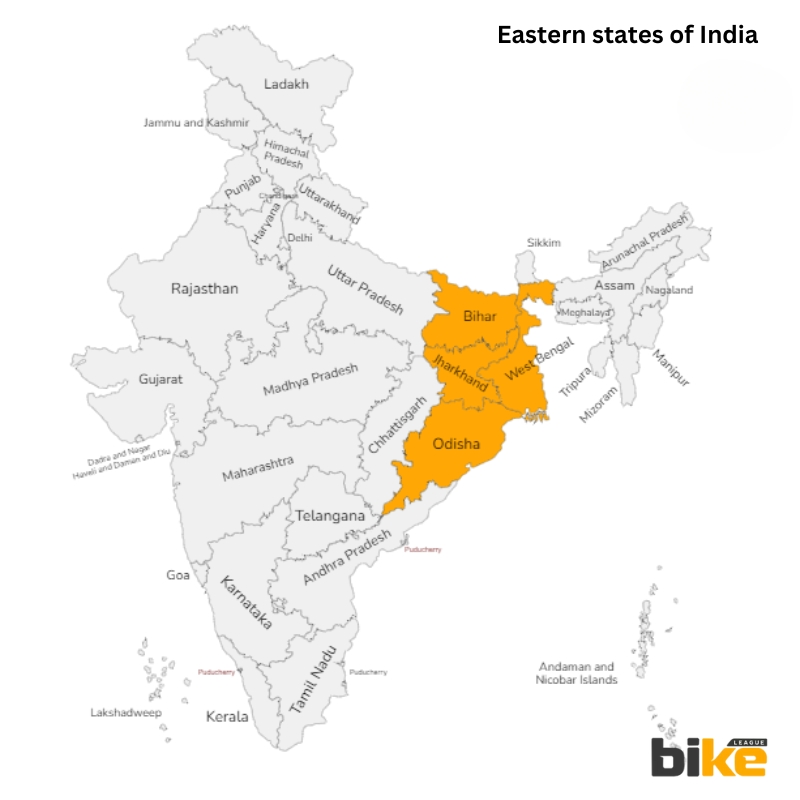
Road Tax for Two wheelers in Eastern states in India
1. Bihar Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Less than Rs. 1 lakh: 8% of the vehicle cost.
- Between Rs. 1 lakh and Rs. 8 lakh: 9% of the vehicle cost.
- Between Rs. 8 lakh and Rs. 15 lakh: 10% of the vehicle cost.
- Above Rs. 15 lakh: 12% of the vehicle cost.
2. Jharkhand Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Upon first registration or up to 1 year of age: 6% of the vehicle’s cost before GST.
- Between 1 and 2 years old: 95% of the tax paid at registration.
- Between 2 and 3 years old: 90% of the tax paid at registration.
- Between 3 and 4 years old: 85% of the tax paid at registration.
- Between 4 and 5 years old: 80% of the tax paid at registration.
- Between 5 and 6 years old: 75% of the tax paid at registration.
- Between 6 and 7 years old: 70% of the tax paid at registration.
- Between 7 and 8 years old: 65% of the tax paid at registration.
- Between 8 and 9 years old: 60% of the tax paid at registration.
- Between 9 and 10 years old: 55% of the tax paid at registration.
- Exceeds ten years: 50% of the tax paid at registration.
3. Odisha Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Below Rs. 5 lakh: 6% of the vehicle’s ex-showroom price.
- Between Rs. 5 lakh and Rs. 10 lakh: 8% of the vehicle’s ex-showroom price.
- Between Rs. 10 lakh and Rs. 20 lakh: 10% of the vehicle’s ex-showroom price.
- Between Rs. 20 lakh and Rs. 40 lakh: 12% of the vehicle’s ex-showroom price.
- Above Rs. 40 lakh: 20% of the vehicle’s ex-showroom price.
4. West Bengal Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- For engines up to 80cc rating: Rs 1,560
- For engines between 80cc and 170cc rating: Rs 3,125
- For engines between 170cc and 250cc rating: Rs 4,685
- For engines over 250cc rating: Rs 6,250
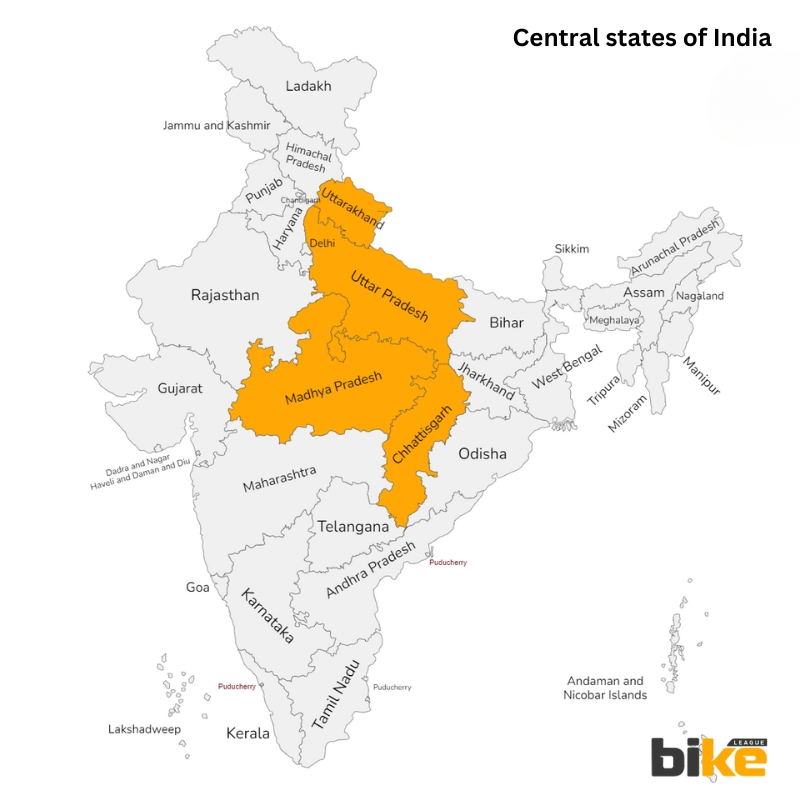
Road Tax for Two wheelers in Central States in India
1. Uttar Pradesh Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Moped with unladen weight below 90.72 kg: Rs. 150.
- Two-wheeler whose value is less than Rs. 0.20 lakh: 2% of the vehicle’s value.
- Two-wheeler whose value is between Rs. 0.20 lakh and Rs. 0.60 lakh: 4% of the vehicle’s value.
- Two-wheeler whose value is between Rs. 0.60 lakh and Rs. 2.00 lakh: 6% of the vehicle’s value.
- Two-wheeler whose value exceeds Rs. 2.00 lakh: 8% of the vehicle’s value.
2. Uttarakhand Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Up to Rs. 10 Lakhs: The road tax is 6% of the vehicle’s price. This category includes most entry-level and mid-range bikes and scooters, making them relatively affordable in terms of tax.
- Over Rs. 10 Lakhs: For vehicles costing more than Rs. 10 lakhs, the tax rate is 8% of the price of the vehicle. This range typically covers higher-end bikes and premium scooters.
Additional Tax Information – Annual Tax
Besides the one-time tax based on the vehicle’s price, Uttarakhand requires all two-wheeler owners to contribute a yearly tax of Rs. 200. This ensures continuous revenue for the state and helps maintain road infrastructure.
3. Chhattisgarh Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Vehicles not exceeding 70 kg: Rs. 8,000 if the vehicle is not over 5 years old, Rs. 6,000 if more than 5 but not more than 15 years old.
- Vehicles exceeding 70 kg but less than 200 cc: Rs. 15,000 if not more than 5 years old, Rs. 8,000 if more than 5 but not more than 15 years old.
- Vehicles exceeding 70 kg and more than 200 cc but less than 325 cc: Rs. 20,000 if not more than 5 years old, Rs. 10,000 if more than 5 but not more than 15 years old.
- Vehicles exceeding 70 kg and over 325 cc: Rs. 30,000 if not more than 5 years old, Rs. 15,000 if more than 5 but not more than 15 years old.
4. Madhya Pradesh Road Tax Rates for Two Wheelers
- Vehicles costing up to Rs 1 lakh: 2% of the vehicle’s cost
- Vehicles costing between Rs 1 lakh and Rs 8 lakhs: 4% of the vehicle’s cost
- Vehicles costing more than Rs 8 lakhs: 6% of the vehicle’s cost
Common Doubts and Misconceptions State Road Tax for Two-wheelers in India
Why does road tax vary from state to state?
Road tax in India is determined by individual states and Union Territories, leading to variations in tax rates. Factors influencing these rates include engine capacity, seating capacity, vehicle age, and weight.
Which states have the lowest and highest road tax rates?
The northeastern region, including Himachal Pradesh, has some of India’s lowest motorcycle road tax rates. In contrast, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Kerala have India’s highest motorcycle road tax rates.
Is road tax mandatory for all bikes?
Yes, all bikes must pay road tax. The RTO collects this tax for the use of roads within a state, while tolls are collected for interstate routes.
Should I pay road tax again if I move to a different state?
Yes, suppose you relocate to a different state. In that case, you must re-register your vehicle with the new state’s RTO and pay the applicable road tax.
What happens if I do not pay the road tax on time?
Failure to pay road tax on time can result in penalties, including fines, vehicle clamping, or impounding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about road tax state-wise for two-wheelers in India
How is Road Tax Calculated for Two-Wheelers?
Road tax for two-wheelers is calculated based on engine capacity, vehicle age, and usage (personal or commercial).
Can Road Tax Be Paid Online?
Road tax can be paid online through the Parivahan or state transport portals. However, this facility is available only in selected states.
What Additional Taxes Are Imposed on Vehicles?
Additional taxes may include environment tax, green tax, cess, road safety tax, and municipality tax, which vary from state to state.
Are There Any Exemptions for Specific Groups?
For example, in Bihar, women drivers with valid driving licenses and registered commercial vehicles are exempt from paying road tax. Various exemptions depend upon the state and vary drastically.
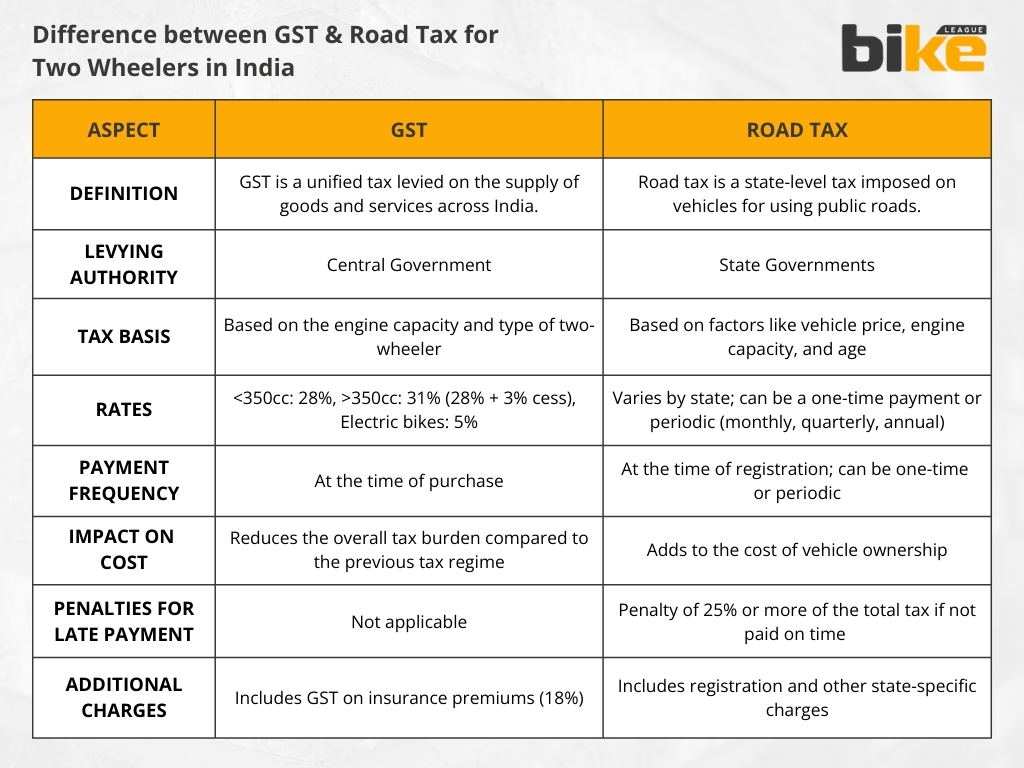
Is GST & road tax the same for two-wheelers in India ?
No. GST is a unified tax system implemented in India in 2017, replacing central and state taxes. The GST rate on two-wheelers depends on the vehicle’s engine capacity.
On the other hand, road tax is a state-level tax imposed on vehicles, including two-wheelers, to fund the maintenance and development of road infrastructure. The road tax rates vary from state to state and are not directly related to the GST rates.
What are the GST Rates on Two Wheelers?
GST rates on two-wheelers vary based on engine capacity. For example, bikes with an engine capacity greater than 350cc attract a GST rate of 31% (including a 3% compensatory cess), while those with less than 350cc attract 28%. Electric bikes have a lower GST rate of 5%.
State-wise official RTO Website Links in India
- Andhra Pradesh official RTO website: AP Transport
- Assam official RTO website: Assam Transport
- Chhattisgarh official RTO website: CG Transport
- Goa official RTO: Goa Transport
- Gujarat official RTO: RTO Gujarat
- Haryana official RTO: Haryana Transport
- Himachal Pradesh official RTO: Himachal Transport
- Jharkhand official RTO: Jharkhand Transport
- Karnataka official RTO: Karnataka Transport
- Kerala official RTO: Kerala MVD
- Madhya Pradesh official RTO: MP Transport
- Maharashtra official RTO: Maharashtra Transport
- Manipur official RTO: Manipur Transport
- Meghalaya official RTO: Meghalaya Transport
- Mizoram official RTO: Mizoram Transport
- Nagaland official RTO: Nagaland MVD
- Odisha official RTO: Odisha Transport
- Punjab official RTO: Punjab Transport
- Rajasthan official RTO: Rajasthan Transport
- Sikkim official RTO: Sikkim Transport
- Tamil Nadu Website: TNSTA
- Telangana Website: Telangana Transport
- Tripura Website: Tripura Transport
- Uttar Pradesh Website: UP Transport
- Uttarakhand Website: Uttarakhand Transport
- West Bengal Website: West Bengal Transport
Other related articles from Bikeleague India
- Two Wheeler Road Tax in India: A Detailed Explanation
- Unlocking the secrets: Factors that impact bike loan interest rate
- The ultimate guide to bike number plates in India – Everything you need to know
- Exploring subsidies & incentives for electric scooters in India
- Simple Energy
Conclusion
Understanding the state-wise road tax for two-wheelers in India is essential for owners to plan their expenses accurately. The tax rates vary significantly across states, influenced by local policies and infrastructure needs. While some states offer exemptions for electric vehicles to promote eco-friendly transportation, others have higher rates to fund extensive road networks.
If you have any other doubts or queries about the Motorcycle road tax in India, email us at bikeleague2017@gmail.com or share your doubts or opinions in the comments section below. We are always eager to help and assist you. Also, here are several social media platforms of Bikeleague India to raise your suspicions.