|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Long story short: Time to know different types of bike clutch like hydraulic clutch, wet clutch, pros and cons, and FAQ about motorcycle clutch.
There is no need for an introduction to clutches. Without a clutch, gear changes are not possible in manual bikes. With technological advancements, several types of clutches are available in the market among various companies, with the basic ones being dry and wet clutches. Motorcycle companies aim to provide buttery smooth gear shifts using clutches with less maintenance and repairs.
Here, we will discuss various bike clutches and their advantages and disadvantages.
What is a bike clutch?
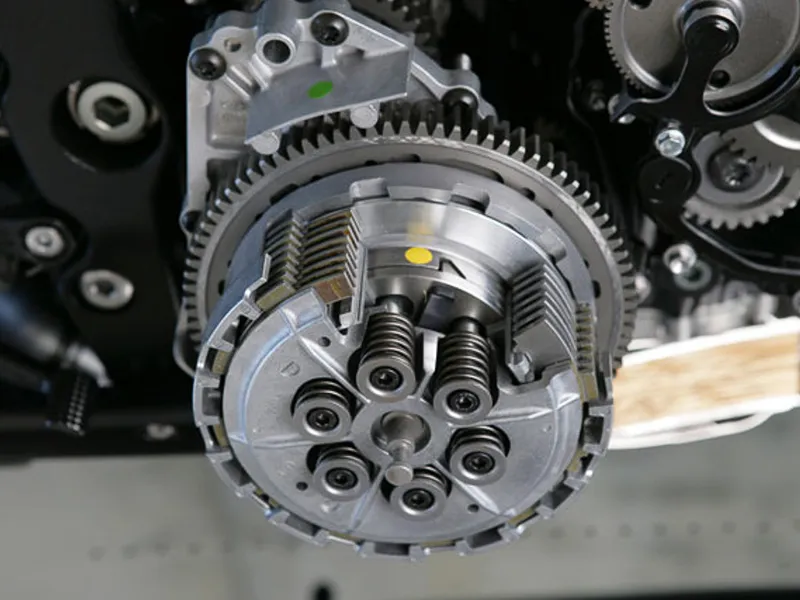
The clutch is a critical component in a motorcycle’s transmission system. Its primary function is temporarily disconnecting the engine from the transmission and drivetrain system, allowing the rider to change gears smoothly. The clutch lever on the left handlebar connects to the circular clutch assembly. There are two main types of clutches: wet clutches, which use engine oil for cooling and lubrication, and dry clutches, which do not require an oil bath.
The connection between bike clutch and gearbox (transmission)
The clutch and gearbox work together to facilitate smooth gear changes. When the clutch lever is pulled, it disconnects the engine from the gearbox, allowing the rider to shift gears without damaging the transmission. Releasing the clutch gradually re-engages the engine with the gearbox, transferring power to the rear wheel.
Different types of bike clutch
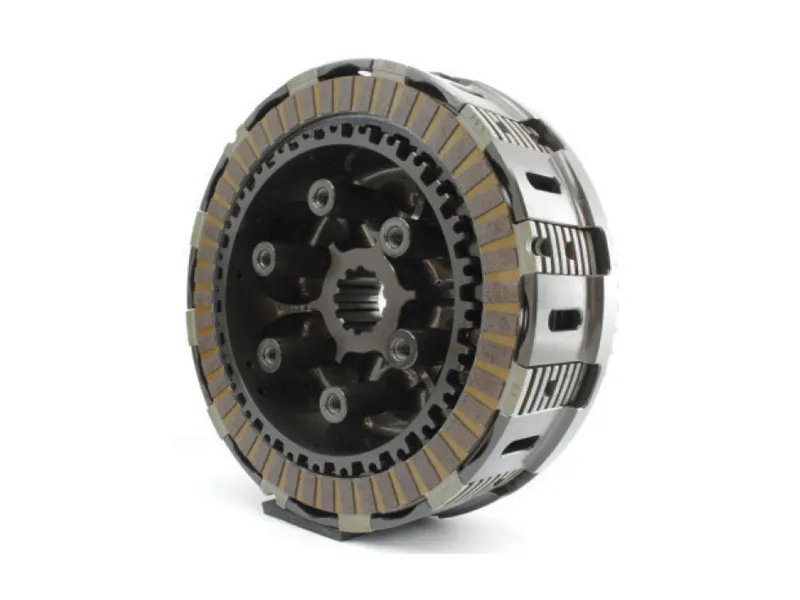
1. Bike Wet Clutch
A wet clutch is the most common clutch type in almost all motorcycles. As the name suggests, the same oil is used for the engine to soak the clutch. This clutch’s primary benefits are its long life and efficiency. Another USP is that power loss due to friction is negligible.
Pros of wet clutch
- Less wear and tear
- Longer life and efficiency
- Negligible friction and power loss
- Cheaper
- Quiet while in operation
Cons of wet clutch
- A slight loss in engine horsepower due to the rotation of the clutch in oil.
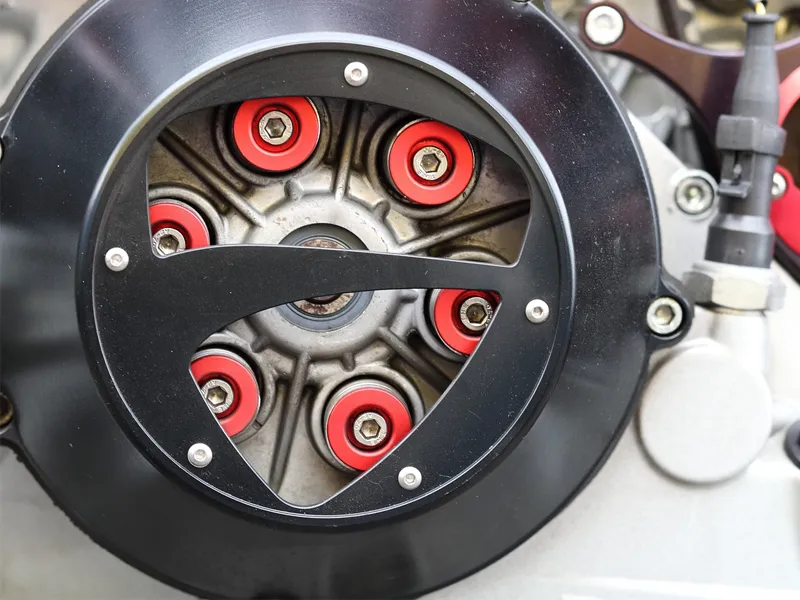
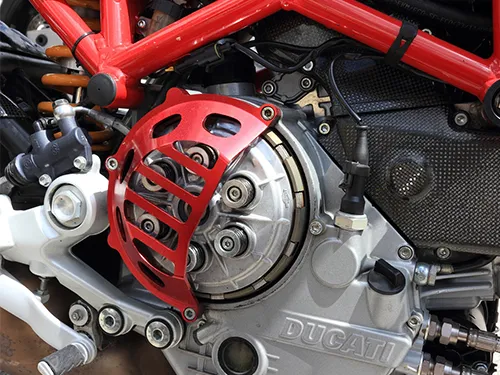
2. Dry Clutch
A dry clutch is one of the different types of bike clutch. The only difference between a wet clutch and a dry clutch is that a dry clutch has no oil and is present entirely outside the bike’s case. A dry clutch setup is mainly found in minimal motorcycle models. Ducati is one company that uses dry clutches.
Pros of dry clutch
- Easy to replace.
- Easy to use.
- No loss of horsepower.
Cons of dry clutch
- Overheating
- Shorter life
- Very noisy
3. Slipper Clutch
The slipper clutch (also known as a back-torque limiter clutch)is one of the different types of clutch that prevents engine over-revving and rear-wheel hop under challenging bike braking scenarios and aggressive gear downshifting. The slipper clutch allows the clutch to slip partially until the engine speed matches the vehicle’s speed. The primary function of a slipper clutch is to control the bike’s rear wheel under hard braking and downshifting scenarios. In vehicles equipped with a standard clutch, the engine braking force is transmitted to the rear wheel via its chain drive, which causes the rear wheel to wobble and may eventually lose traction. Some models of KTM and Bajaj have slipper clutch equipped with the engine.
Pros of slipper clutch
- Prevents rear wheel lockup
- Absorbs engine braking force
- Ability to perform aggressive downshifts during cornering and emergencies.
- Reduces wear and tear on the engine and transmission
- Prevents accidental downshifts
- Excellent performance-wise
Cons of slipper clutch
- Mechanically complex technology
- Expensive
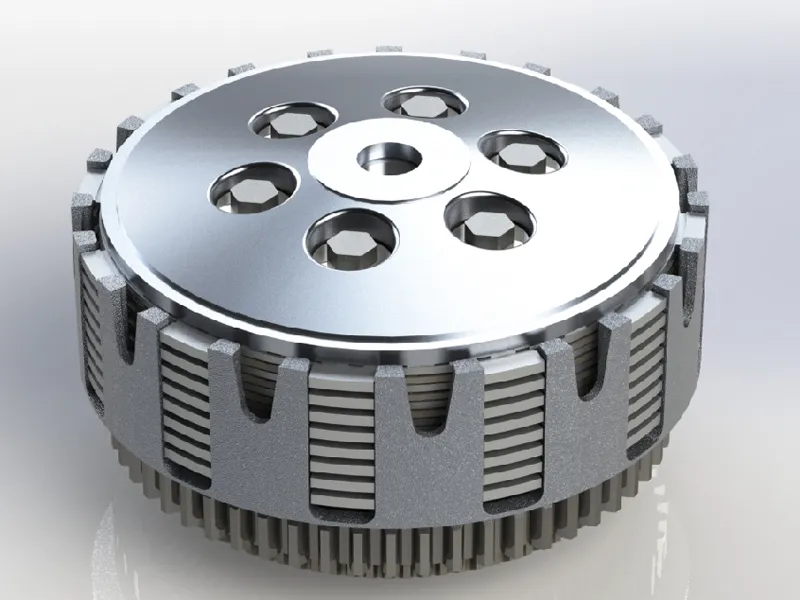
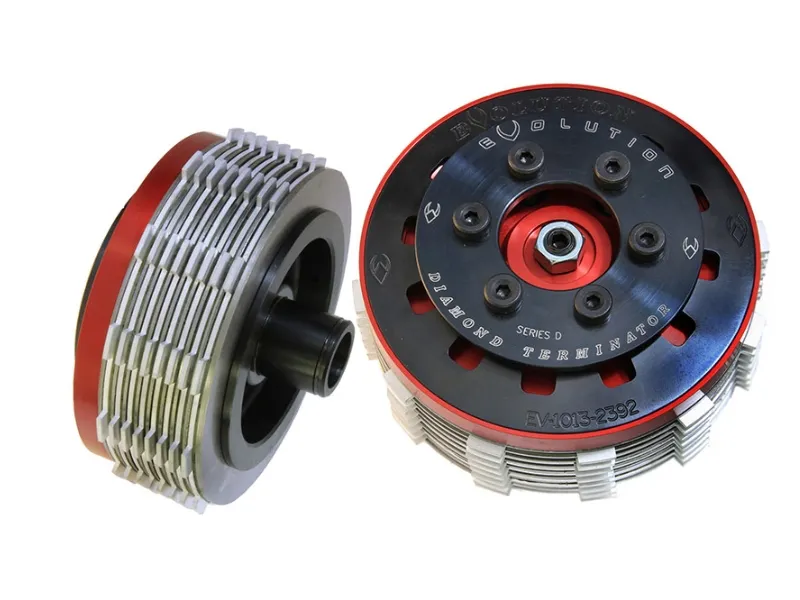
4. Multi-plate bike Clutch
The multi-plate clutch is the most common type of clutch used in motorcycles. It can be used both as a wet and dry clutch unit. These types of clutches use several interleaved driven and friction plates placed in a standard hub. The main USP of a multi-plate clutch over a single-plate clutch is the high torque transmitting capacity. A multi-plate clutch is smaller than a single-plate clutch for a given torque capacity. Hence, it is used mainly in compact vehicles like motorcycles, etc. Let’s compare both multi-plate clutch and single-plate clutch below.
Pros of Multi-plate clutch
- Ability to transmit a high amount of torque
- The smaller size compared to single plate clutch
Cons of Multi-plate clutch
- Expensive
- Heavy
- Clutch engagement is not instantaneous
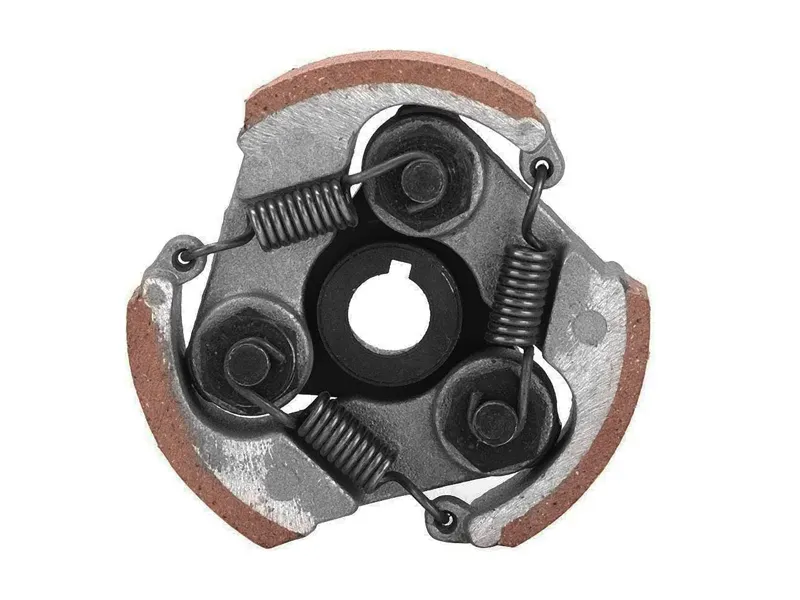
5. Centrifugal Clutch (Automatic Clutch)
Centrifugal clutches are used in mopeds and scooters, as the engine rpm defines the engagement or disengagement of the clutch. This clutch type works similarly to the Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT). It works on the principle of centrifugal force exerted on a revolving mass, which acts as an attractive force. This clutch is placed between the engine shaft and the transmission shaft. One side of the clutch is connected to the engine crankshaft, and the other is connected to the gearbox shaft, chain, or belt.
Pros of Centrifugal clutch
- Automatic and simple to use
- Low in price and less maintenance
- Prevents the engine from stalling
Cons of Centrifugal clutch
- Not able to transmit a considerable amount of torque
- Power loss due to friction and slipping
- Overheating issue
- Limited power transmission due to slippage
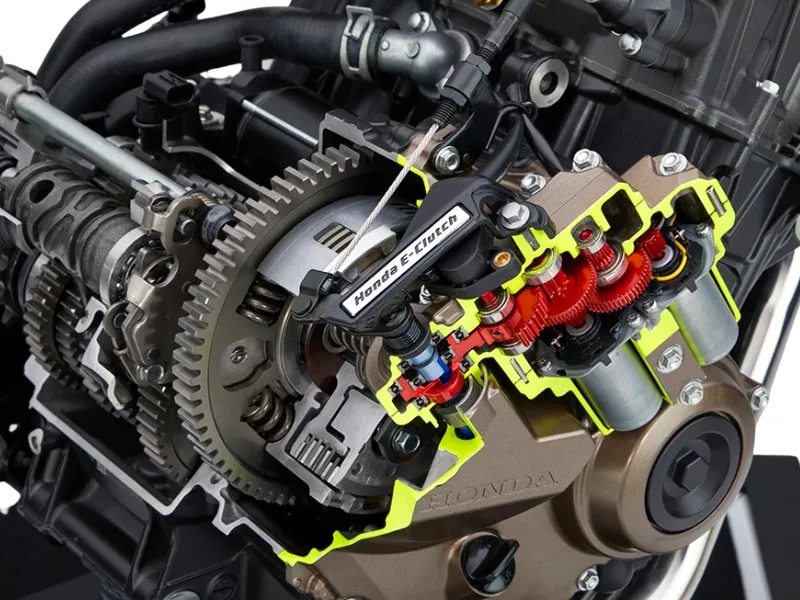
6. Electronic Clutch
An electronic clutch (E-Clutch) is an advanced clutch system among various clutch types that automates clutch operation while maintaining the traditional gear-shifting mechanism. This technology allows automatic clutch control during starting, stopping, and shifting, with the option for manual clutch operation when desired.
Pros of Electronic Clutch
- Ease of Use: Simplifies gear shifting without manual clutch control, making it nearly impossible to stall the engine.
- Flexibility: Offers the option for manual clutch operation, providing a balance between automatic and manual control.
- Convenience: Ideal for commuting and riders with hand strength issues, such as older or those with arthritis.
Cons of Electronic Clutch
- Complexity: Increased complexity and weight can affect the bike’s performance and maintenance.
- Potential for Failure: More electronic components can fail, leading to potentially costly repairs.
7. Diaphragm Spring Clutch
The diaphragm spring clutch uses a single diaphragm spring to provide clamping pressure. This clutch type is typically found in heavy-duty motorcycles because it offers higher clamping pressure than coil springs. The diaphragm spring clamps in a full circle on the clutch plates, ensuring even pressure distribution and efficient engagement. This clutch type is more compact and lighter than traditional coil spring clutches.
Pros of Diaphragm Spring Clutch
- Compact Design: More compact and lighter, resulting in a smaller clutch housing and weight reduction.
- Consistent Pressure: Provides consistent pressure and smoother operation, enhancing the riding experience.
- Dual Functionality: The diaphragm spring acts as both the clamping spring and the release lever, reducing the number of parts needed.
Cons of Diaphragm Spring Clutch
- Cost: It can be more expensive to replace compared to coil spring clutches.
- Size Requirements: To achieve a higher coefficient of friction, the size and diameter of the diaphragm need to be increased, which can complicate the design.
8. Constant-Mesh Clutch
A constant-mesh clutch meshes all gears, allowing for smoother and quicker gear changes. This type of clutch is commonly used in modern motorcycles with advanced transmissions.
Pros of Constant-Mesh Clutch
- Smooth Gear Changes: Allows for quicker and smoother gear changes, enhancing the riding experience.
- Reduced Wear: Reduces wear on gears, leading to a longer lifespan for the transmission components.
Cons of Constant-Mesh Clutch
- Complexity: More complex and can be more expensive to repair due to the intricate design and precise engineering required.
9. Cable-Operated Clutch
The cable-operated clutch uses a cable mechanism to engage and disengage the clutch. The rider manually operates This clutch through a lever connected to the clutch cable. Cable-operated clutches are present in older bikes and classic motorcycle models. They are best for their simplicity and ease of maintenance.
Pros of Cable-Operated Clutch
- Lower Cost: Cable clutches are generally cheaper to purchase and maintain.
- Simple Maintenance: Maintenance tasks such as cable lubrication are straightforward and can be done easily by the rider.
- Adjustability: Riders can manually adjust the clutch engagement point to their preference, providing a customizable feel.
- Preferred by Some Riders: Some experienced riders, including professional racers, prefer the tactile feedback and modulation of cable clutches.
10. Bike Hydraulic Clutch
Among the different types of bike clutches, the hydraulic clutch boasts smoother operation and reduced effort due to the use of hydraulic fluid. A hydraulic clutch system uses a fluid-filled reservoir attached to the bike clutch lever. When the lever is pulled, the fluid pressure is transmitted through a hydraulic line to a bike slave cylinder, which disengages the clutch. The fluid used in hydraulic systems is almost incompressible, ensuring efficient energy transfer.
Pros of Bike Hydraulic Clutch
- Ease of Use: Hydraulic clutches generally have a lighter pull, making them easier to operate, especially in heavy traffic. This reduces rider fatigue during long rides compared to other different clutch types.
- Self-Adjusting: These systems are self-adjusting, meaning they automatically compensate for wear and tear, ensuring consistent performance.
- Low Maintenance: Hydraulic clutches are virtually maintenance-free, requiring only periodic fluid changes rather than regular cable lubrication.
- Smooth Operation: The hydraulic system provides smoother and more precise control over the clutch, which can benefit fine-tuning and modulation.
Cons of Hydraulic Clutch
- Higher Initial Costs: Hydraulic clutches’ initial cost and installation are higher than cable-operated systems.
- Complex Maintenance: While they require less frequent maintenance, when issues do arise, such as fluid leaks or seal damage, repairs can be more complex and costly.
- Fluid Management: Requires regular fluid change as it can absorb moisture, affecting performance.
- Engagement Feel: Some riders find the engagement point of hydraulic clutches less intuitive and harder to get used to.
11. Coil Spring Clutch
Coil spring clutches, commonly found in road bikes, use multiple coil springs to provide the necessary tension for clutch engagement. These springs are positioned between the diaphragm springs and help engage and release the clutch during gear changes. Adjusting the force of the coil springs modifies the clutch’s performance.
Pros of Coil Spring Clutch
- Consistent Performance: Coil springs provide consistent tension, ensuring reliable clutch operation.
- Widely Used: They are commonly used on road bikes and general motorcycles.
Cons of Coil Spring Clutch
- Maintenance Required: The springs can wear out over time and may need to be replaced.
- Not Ideal for High-Performance Applications: They may not provide the same level of performance as diaphragm spring clutches in high-torque situations.
FAQ related to different types of bike clutch
1. What are the benefits of a wet clutch over a dry clutch?
Wet clutches are more durable, quieter at idle, and can sustain more abuse compared to dry clutches. They are better suited for stop-and-go traffic and general road use.
2. Which clutch is the best for racing or performance bikes?
The slipper clutch is the best, as it can withstand aggressive downshifts, higher engine braking force, and rear wheel lockup than other bike clutch types.
3. Is partial or half-clutch riding good for transmission?
No. Half-clutch riding can cause premature wear to parts and damage to the transmission.
4. Does using a bike clutch frequently affect mileage?
Yes. Using the clutch frequently while driving increases fuel consumption. The engine consumes more fuel when the clutch is pressed but rather when a gear is engaged.
5. Does bike clutch wear affect mileage?
Yes. As the motorcycle’s clutch starts to wear, it slips to other gears, affecting fuel efficiency.
6. What is the difference between a bike hydraulic clutch and a cable-operated clutch?
A hydraulic clutch operates using hydraulic fluid, providing smoother and more precise control over the bike. It is often found in touring and heavy-duty bikes. In contrast, a cable-operated clutch relies on a mechanical cable mechanism, which is more common in older and classic models.
7. What are the benefits of a wet clutch over a dry clutch?
Wet clutches are more durable, quieter at idle, and can sustain more abuse compared to dry clutches. Stop-and-go traffic and general road use motorcycles wet clutches.
8. How does a coil spring clutch differ from a diaphragm spring clutch?
A coil spring clutch, commonly found in road bikes, uses multiple coil springs to provide tension. On the other hand, a diaphragm spring clutch uses a single diaphragm spring. Heavy-duty motorcycles use this type of bike clutch for its consistent pressure distribution.
Other related articles from Bikeleague India
- Bike wash – Different types, procedures, precautions, FAQ
- Braking in motorcycle – All expert tips for bikers
- Motorcycle helmet in India – All in one buying guide
- motorcycle swingarm varieties exploring different types/
- The Ultimate Guide to Motorcycle Suspension: Everything You Need to Know
Conclusion
We have discussed different types of bike clutches, their pros and cons, and some related FAQs. If you have any other questions or queries, email us at bikeleague2017@gmail.com. You can also share your doubts or opinions in the comments section below. We are always eager to help and assist you. Also, here are several social media platforms of Bikeleague India to raise your suspicions.