|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Long story short: There are various motorcycle engine types, From single-cylinder to V-twin. Learn about the different types and their pros and cons in this guide.
Motorcycle engines form the heart of a motorcycle, where all the ingredients come together and produce the energy to move the bike forward. However, technological advancements have resulted in drastic changes in engine architecture, and various companies are still developing innovative engine features.
With rising fuel prices and stricter emission norms, companies are forced to make changes within the engine for the greater good. Several companies have brought different types of motorcycle engines in their business journey, and we have witnessed the same. Here, we will discuss the various types of motorcycle engines based on the number of cylinders and their configuration with examples and pictures.
Key Takeaways
- There are mainly 5 types of motorcycle engines – Single, Twin, Triple, Four and Six
- In Two-cylinder engine types, there are four variations – Parallel Twin, V Twin, L Twin and Boxer
- In Four-cylinder engine types, there are two variations – Inline Four and V-Four
- Six-cylinder engine is also known as Straight six engine / Flat-Six Engine
Different types of motorcycle engines
The major engine types in motorcycles are as follows
- Single cylinder engine
- Two / twin cylinder engine
- Triple cylinder engine
- Four cylinder engine
- Six-cylinder engine
1. Single-cylinder motorcycle engine
As the name suggests, only a single piston provides the necessary power for your motorcycle. This engine type is used in entry-level and small-displacement motorcycles as it is inexpensive, compact, and lightweight. Performance from this engine is limited compared to other engine types. Still, it provides enough performance for city rides and gives good mileage figures.
Example: Hero Hf 100
Pros of single cylinder engine
- Lightweight
- Fuel efficient
- Inexpensive
- Compact
Cons of single cylinder engine
- Limited performance
- Higher vibrations in top speed
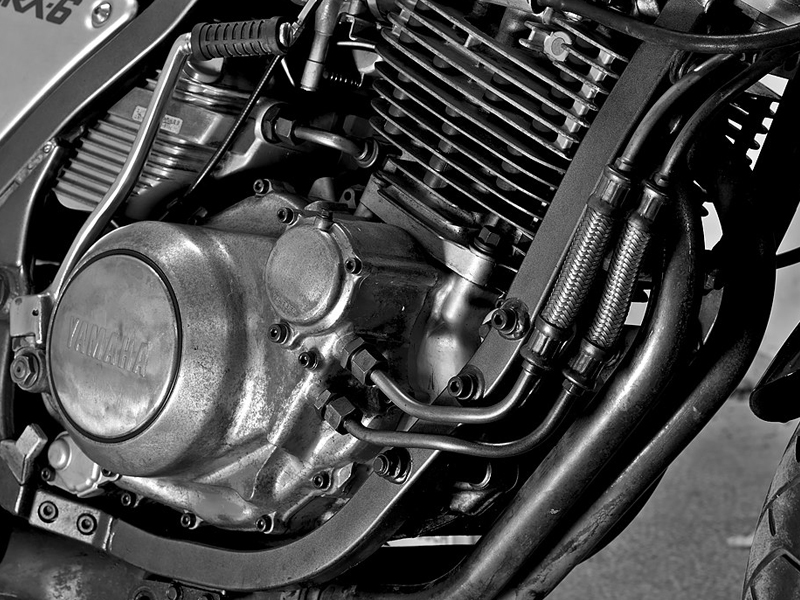
2. Two-cylinder bike engine
Within the two-cylinder engine, there are four types according to various configurations.
- Parallel Twin
- V Twin
- L Twin
- Boxer
1. Parallel twin
In a parallel-twin engine, both cylinders are arranged along a common crankshaft. This type of engine is generally present in medium and high-displacement models. Several 200-300cc entry-level sports bikes use parallel twin-engine configurations. Honda, Yamaha, Kawasaki, etc., have many parallel twin engine models.
Example: Kawasaki Ninja 300
Pros of Parallel Twin Engine
- Excellent performance
- Lower vibrations
- Excellent torque
Cons of Parallel Twin Engine
- Higher vibrations compared to other premium engine types
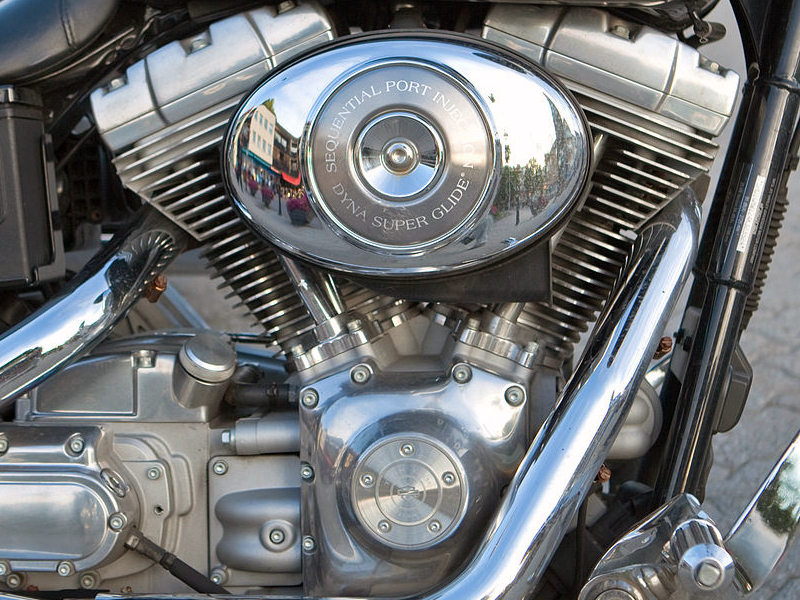
2. V Twin
Here, two cylinders are arranged to form a V over a common crankshaft. Harley Davidson is a company that widely uses V Twin engines. Most dedicated touring models use V Twin configurations, providing excellent torque and comfort for long hauls.
Example: Harley Davidson Fat Boy
Pros of V Twin engine
- Excellent performance
- Lower vibrations
- Excellent torque
- Good comfort
Cons of V Twin engine
- Higher vibrations compared to parallel twin
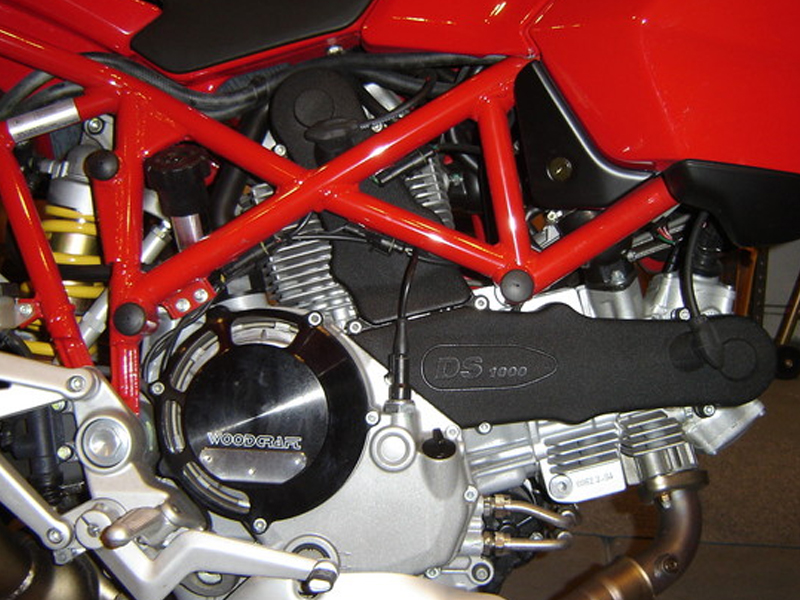
3. L Twin motorcycle engine
Here, two cylinders are arranged to form an L over a common crankshaft with a 90-degree angle between them. Ducati is a company that widely uses L Twin engines. Several Ducati models use L Twin to gain high-revving capabilities.
Example: Ducati Scrambler Icon
Pros of L Twin engine
- Same as V twin engines
- Very low vibrations compared to V Twin
- Best for high revving
Cons of L Twin engine
- Same as V twin engines
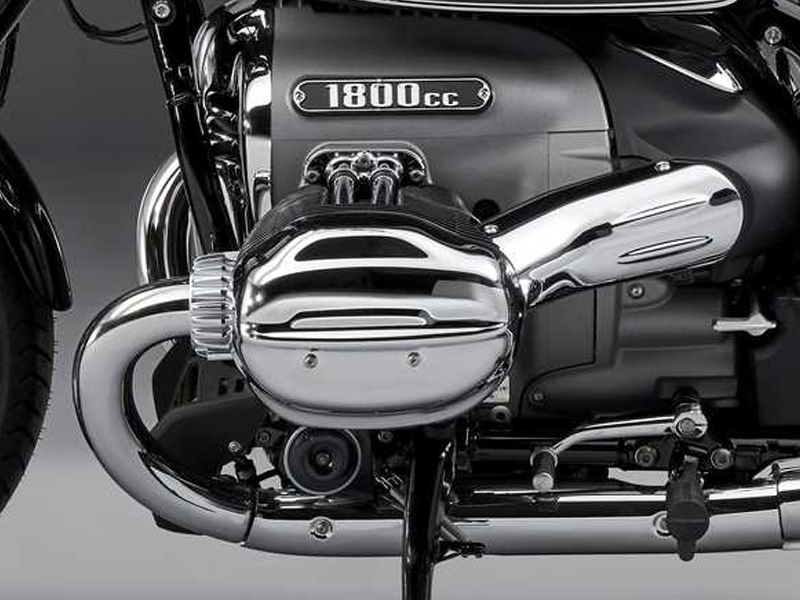
4. Boxer / Flat Twin Bike Engine
Flat twin or boxer engines use a “boxer” configuration, where each pair of opposing pistons move inwards and outwards simultaneously like boxing competitors punching their gloves together before a fight. These engines are present on many BMW models.
Example: BMW R 1250 GS
Pros of Boxer engine
- ow vibration
- Excellent performance
- Superb air cooling
- No balance shaft is required
Cons of Boxer engine
- Less fuel efficient
3. Triple-cylinder motorcycle engine
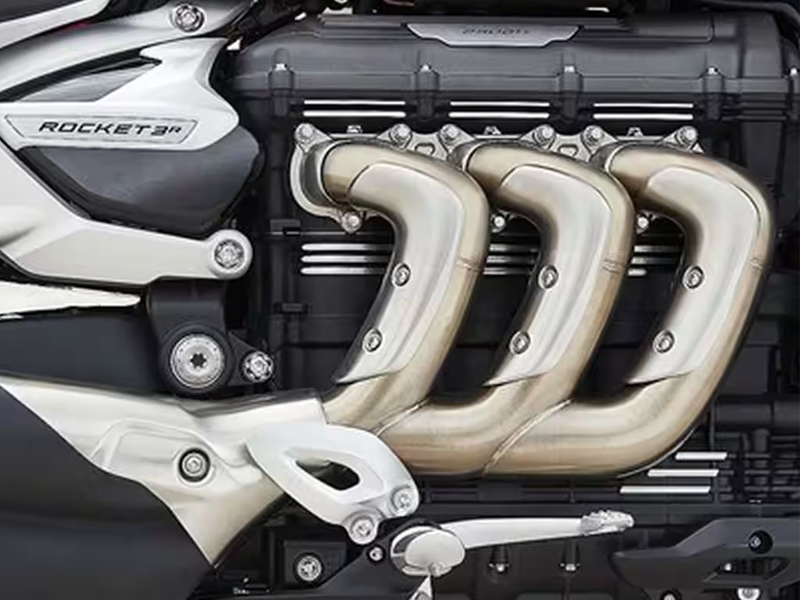
A straight-three engine, inline-triple, or inline-three is a three-cylinder piston engine with cylinders arranged along a common crankshaft. Triple-cylinder engines are much smoother than a V-twin, narrower, and lighter than an inline-four. They are mainly found in Triumph motorcycles.
Example: Triumph Rocket 3R
Pros of triple cylinder Engine
- Low vibration
- Excellent performance
- Superb comfort
Cons of triple cylinder Engine
- Less fuel efficient
4. Four cylinder engine
Four-cylinder motorcycle engines are popular due to their balance of power, smoothness, and reliability. Within the four-cylinder engine, there are two types according to various configurations.
- Inline Four Engine
- V-Four Engine
1. Inline Four Engine
Straight or inline-four engines have all cylinders aligned in one row and no offset. Most premium racing models from Honda, Suzuki, Kawasaki, etc., come with inline-four engines.
Example: Kawasaki Z 900
Pros of Inline Four Engine
- Low vibration
- Excellent performance
- Superb comfort
Cons of Inline Four Engine
- Large dimensions & size
2. V-Four Engine
A V4 engine is a four-cylinder piston engine in which the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration. Ducati has several V2 and V4 engine models, such as the Panigale V4S and the Streetfighter V4.
Example: Ducati Multistrada V4 S
Pros of V-Four Engine
- Low vibration
- Excellent performance
- Superb comfort
Cons of V-Four Engine
- Complexity in construction
- Heavier
5. Straight six engine / Flat-Six Engine
Straight-six engines are like flat-twin / boxer engines but with more cylinders. These engines are rare and rarely seen outside large touring models. Straight-six engines have three cylinders horizontally on either side of the engine.
Example: Honda Goldwing
Pros of Straight six engine
- Excellent performance
- Superb comfort and smoothness
- Lots of power and torque
- Provides excellent balance and stability
Cons of Straight six engine
- Expensive
- Heavier
- Larger in dimensions
FAQ related to different types of motorcycle engines
1. Which engine type has the most fuel efficiency or mileage?
The single-cylinder engine has the highest fuel efficiency and is used in small displacement and entry-level motorcycles.
2. Is there a relation between the number of cylinders and mileage on a motorcycle?
Yes. The number of cylinders and fuel efficiency are inversely proportional.
3. Is there a relation between the number of cylinders and performance on a motorcycle?
Yes. The number of cylinders and fuel efficiency are directly proportional.
4. Which motorcycle engine type produces the most torque?
V twin configuration produces the most torque; within these, the V twin with the most cylinders produces more torque.
5. What is the advantage of the L Twin engine over the V Twin engine?
The L twin engine avoids many vibrations compared to V twin engines, which is a real boon for engines that rev very high.
10 Common Myths About Motorcycle Engine Types
Myth #1: More Cylinders Always Mean Better Performance
Fact Check: False
Multi-cylinder engines provide smoother operation, but they’re not always better. Different engine configurations serve various purposes. Single and twin-cylinder engines can perform well for specific riding needs. Engine efficiency depends on several factors beyond just the number of cylinders.
Myth #2: Single-Cylinder Engines Are Only for Budget Bikes
Fact Check: False
Single-cylinder engines are used in various motorcycle segments, from entry-level to premium models. They are common in adventure and off-road bikes, and some premium motorcycles up to 700cc feature this configuration. These engines provide excellent low-end torque and are more straightforward in design.
Myth #3: Four-Stroke Engines Are Always More Fuel-Efficient
Fact Check: Partially True
Fuel economy can vary due to several factors. The move to 4-stroke engines in India aimed at improving efficiency and meeting environmental standards. Riding style and maintenance greatly influence fuel efficiency. Additionally, modern engine technology is key to achieving better efficiency.
Myth #4: Premium Motorcycles Must Have Large-Displacement Engines
Fact Check: False
The premium motorcycle segment includes various engine sizes. Motorcycles with engine capacities between 250cc and 500cc comprise a large part of this market. Premium features and build quality depend not solely on engine size, as many premium motorcycles prioritize technology and refinement over displacement.
Myth #5: V-Twin Engines Are Only for Cruisers
Fact Check: False
V-twin engines are found in various motorcycle types and provide strong low-end torque. Many sport and adventure bikes utilize V-twin configurations. The engine’s character, rather than the bike type, dictates the configuration choice.
Myth #6: Bigger Engines Always Need More Maintenance
Fact Check: False
Maintenance needs vary based on several factors beyond engine size. Modern engines use advanced technology to enhance reliability, and predictive maintenance techniques can optimize service intervals. Ultimately, regular maintenance is crucial for longevity, regardless of engine size.
Myth #7: All Multi-Cylinder Engines Are Fuel-Hungry
Fact Check: False
Fuel efficiency is influenced by engine design and technology. Modern multi-cylinder engines often achieve high fuel efficiency. Riding style and maintenance play a crucial role in fuel consumption. New technologies enhance efficiency in all engine types.
Myth #8: High-Performance Engines Can’t Be Used Daily
Fact Check: False
Thanks to advanced technology that enhances reliability and usability, high-performance engines are now built for regular use. Maintenance is more manageable, and many high-performance bikes serve well as daily riders.
Other related articles from Bikeleague India
- Different types of motorcycles explained
- Which bike chassis is right for your riding style
- Motorcycle riding style – How to choose your perfect bike
- Electric motorcycles & scooters in India: Examining the pros & cons
- BMW R 12 nineT
Conclusion
We have discussed various types of motorcycle engines based mainly on engine cylinders and their configuration. Now, let’s summarize the different kinds of motorcycle engines.
- Single cylinder
- Parallel Twin
- V Twin
- L Twin
- Boxer / Flat Twin
- Triple cylinder
- Inline Four
- V-Four
- Six cylinder
If you have any other questions or queries, email us at bikeleague2017@gmail.com. We are always eager to help and assist you. Also, here are several social media platforms of Bikeleague India to raise your suspicions.