|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Long story short: Here, we will discuss the types of motorcycle suspension, front and rear suspension, types, maintenance, and FAQs related to bike suspension.
Motorcycle suspension or two-wheeler suspension acts as the balance system like it is for humans. In India, not all places have paved roads, so the ride will be bumpy and uneven. So, to counter these types of roads, a good suspension setup is mandatory on our bikes. The suspension setup does the job of soothing and making your ride comfortable on these roads.
While selecting a two-wheeler, you need to make sure a good suspension is present. It serves a dual purpose: contributing to the vehicle’s handling and braking and providing safety and comfort to the motorcycle. So here we will discuss in detail the types of front and rear motorcycle suspension, maintenance, and FAQs related to bike suspension.
Different types of motorcycle suspension
Motorcycle suspension can be categorized into two:
- Front motorcycle suspension setup
- Rear motorcycle suspension setup
In this, for each setup, there are different types, and they are
Different types of front motorcycle suspension
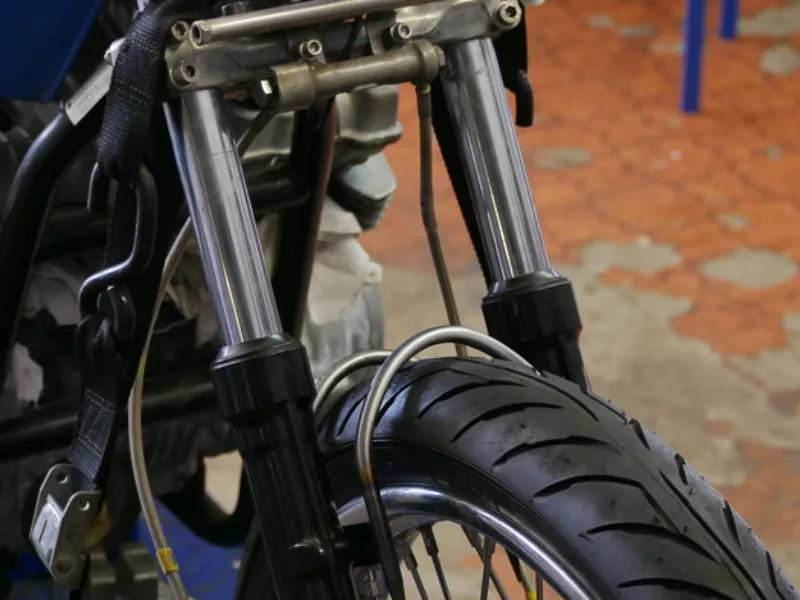
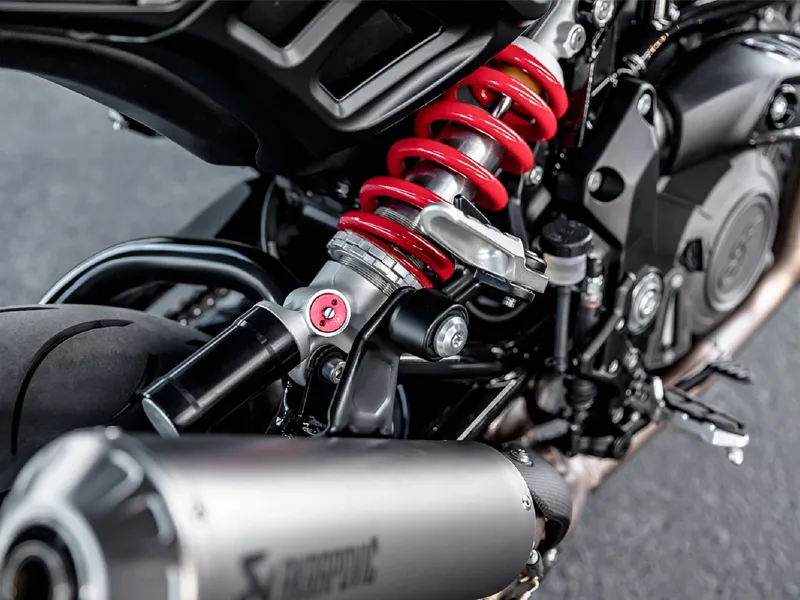
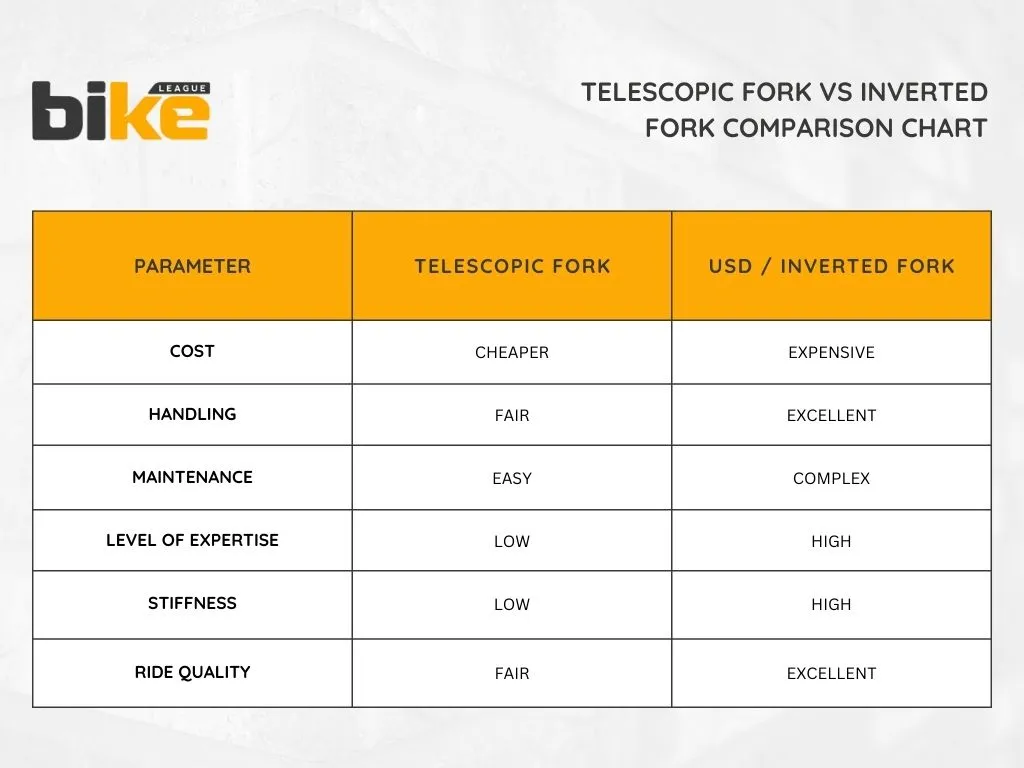
1. Telescopic forks
These forks are the most common front suspension system, consisting of two fork tubes with internal springs and dampers. When the front wheel encounters a bump, the fork tubes compress, allowing the springs and dampers to absorb the impact.
Pros of telescopic forks
- Simplicity and ease of maintenance
- Less expensive
Cons of telescopic forks
- Low level of stiffness compared to USD forks
- Low precision level compared to USD forks
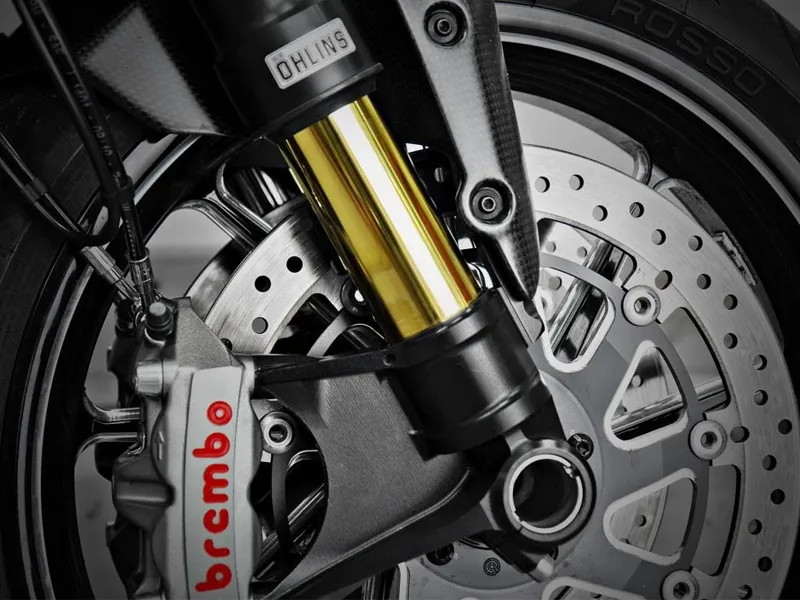
2. Upside-down telescopic forks (USD) or inverted forks
USD forks are a more advanced version of telescopic forks, with the stanchion tubes inverted for improved performance. They are similar to telescopic forks but with reduced unsprung weight and better mass distribution, leading to enhanced handling. This makes them a popular choice among front motorcycle suspension types.
Pros of Upside-down forks
- High level of stiffness compared to telescopic forks
- High precision level compared to telescopic forks
- Better handling compared to telescopic forks
Cons of Upside-down forks
- Expensive
- Tough to repair if an oil leak is there
- Need extra care and maintenance
Different types of rear motorcycle suspension
1. Spring-loaded hydraulic suspension
Among rear motorcycle suspension types, this system uses springs and hydraulic dampers to absorb shocks from the rear wheel. The springs compress while the hydraulic dampers regulate the compression and rebound, ensuring a smoother ride.
Pros of Spring-loaded hydraulic suspension
- Good for absorbing large bumps, adjustable preload and damping
Cons of Spring-loaded hydraulic suspension
- Can be heavy, requires regular maintenance
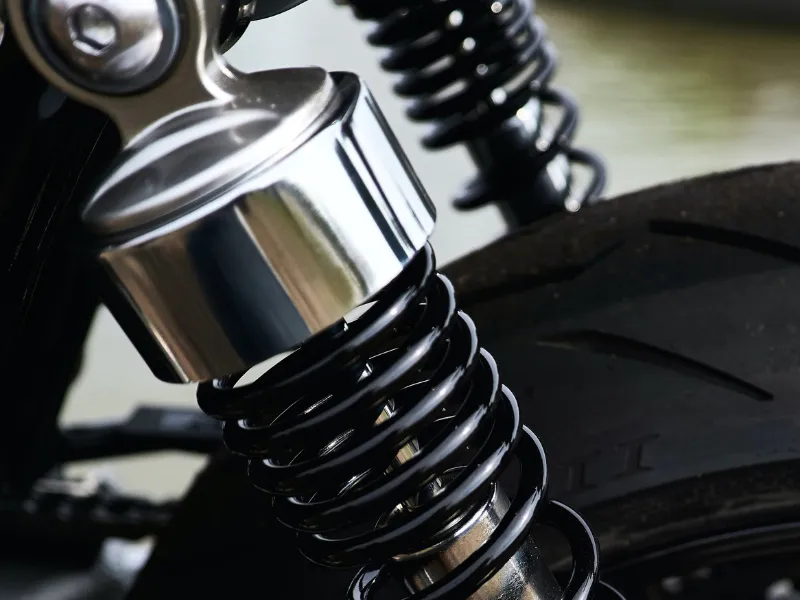
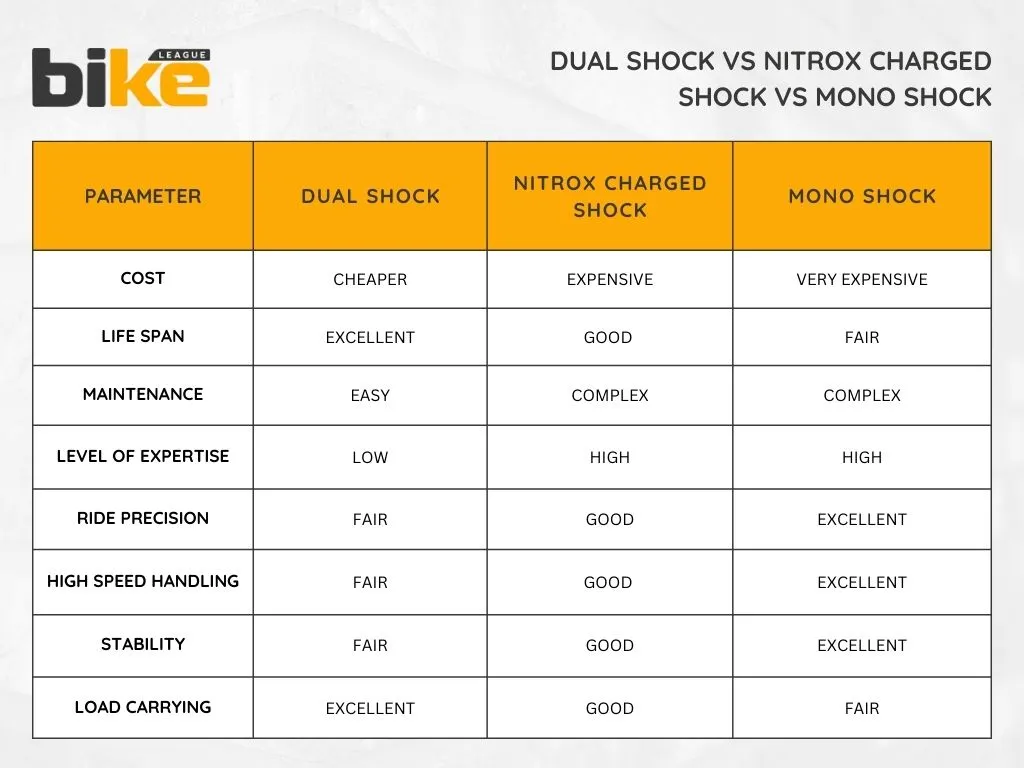
2. Dual or Twin shock absorber suspension
As the name suggests, two shock absorbers are in the motorcycle’s rear section. It is a type of spring-loaded hydraulic suspension found mainly in cruisers and touring bikes. Both shocks work in tandem to absorb impacts from the rear wheel.
Pros of twin shock absorber suspension
- Easier to maintain
- Offers a supple ride
- Cost-effective
Cons of twin shock absorber suspension
- Variable damping from two shocks as they work independently
- It offers less stability while cornering
- It offers less stability at high speeds
- In extreme conditions, bubbles are formed in damping oil, known as cavitation, which affects damping
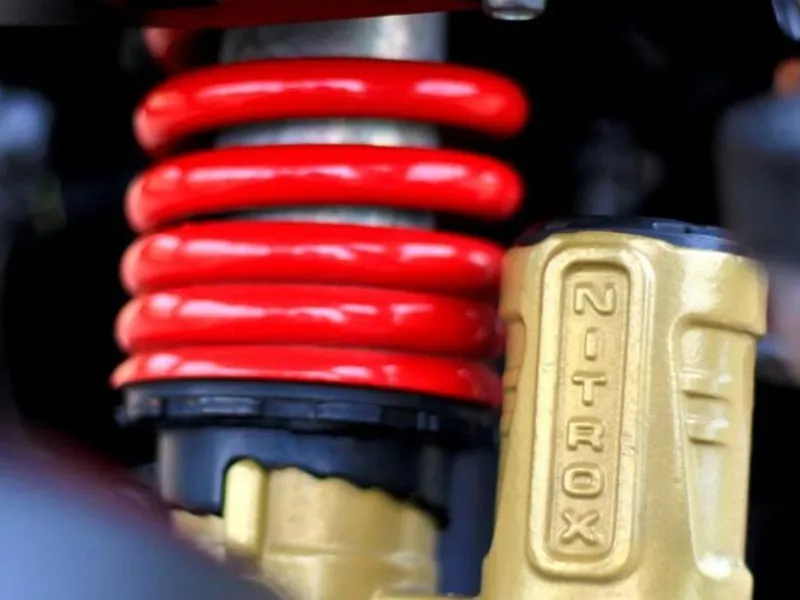
3. Gas-filled or Nitrox charged shock absorber
These shocks use gas (usually nitrogen) to enhance damping performance. The gas helps maintain consistent damping performance by reducing the likelihood of cavitation (formation of air bubbles) within the damper.
Pros of Nitrox charged shock absorber
- Prevents cavitation issues
- Reduced bouncing on irregular surfaces
- Efficient dissipation of heat on the tube
- Offers better stability in corners and at high speeds
Cons of Nitrox charged shock absorber
- Expensive than a twin shock absorber
- Complicated with repair and maintenance
4. Mono shock absorber
Mono-shocks are single shock absorbers located centrally, often under the seat, offering advanced performance. The shock absorber connects to the swingarm and frame, providing better weight distribution and handling.
Pros of mono shock absorber suspension
- Superb cornering capability and handling
- Excellent high-speed stability and rideability
- Easy to tune and adjust
- Precise damping
Cons of mono shock absorber suspension
- High maintenance
- Cannot carry the excess load
- Shorter life span compared to other suspension setups
- Expensive
FAQ related to different types of motorcycle suspension
1. How does motorcycle suspension work?
Motorcycle suspension combines spring and shock absorber to isolate the chassis and rider from road imperfections. Any suspension setup needs three things – a spring to absorb bumps & shocks, a way to dampen the motion of the spring and enough range of motion to allow the first two components to function. The shock absorbers resist movement and, in doing so, tend to quiet the oscillations incurred by the frame. At the same time, the spring absorbs bumps and shocks.
2. How can we adjust motorcycle suspension?
In most motorcycles, there is an option to adjust motorcycle suspension to a softer or harder suspension feel in the rear section. There will be a nut or a screw for the same to adjust. For detailed instructions, please refer to the owner’s manual.
3. How can we adjust motorcycle suspension according to weight?
This is not a DIY task and requires expertise.
4. Which is the best motorcycle suspension setup for performance-oriented bikes?
In the front section, go for USD forks, while in the rear, mono shocks are the best. It is a significant performance bonus if mono-shock comes with a gas canister.
5. Which motorcycle suspension setup is best for heavy riders and loads?
Go for dual shock absorbers with gas canisters in the rear. At the same time, in the front section, both setups, telescopic and inverted forks, are acceptable.
6. When to change and repair the two-wheeler suspension?
In 99% of cases, suspension change is not required other than in significant accidents. However, a regular shift in fork or damping oil is needed as per the service manual.
7. What is Preload on motorcycle suspension?
It refers to the initial position of suspension with the motorcycle’s weight and rider acting on it.
8. What is Rebound on two-wheeler suspension?
Rebound is the rate at which the suspension can extend and return to its normal position once the motorcycle has encountered a bump.
9. What is Brake dive on motorcycle suspension?
When the brakes are applied, the front wheel causes the bike’s front end to go lower, resulting in the compression of the forks, known as brake dive.
10. What is damping on a two-wheeler suspension?
Damping controls or stops the spring’s oscillation when it compresses or rebounds.
11. What is motorcycle suspension sag?
Suspension sag is the amount of suspension travel used when sitting on your bike in a natural riding position.
12. What is a soft suspension setup?
Soft suspension gives the vehicle a plush low-speed ride and is not rigid. Even when the road gets rough, the ride will not be uncomfortable. This suspension is ideal for commuting but is not recommended for high-speed and enthusiastic riders.
13. What is a hard suspension setup?
A complex suspension setup is the exact opposite of a soft suspension setup. This setup is recommended for high-speed and enthusiastic riders where the handling is excellent. The downside of this setup is that the rider can feel all bumps and irregularities on the road.
14. What is a medium suspension setup?
A medium suspension setup sits between a soft and firm one. It provides a good balance of ride and handling. It gives the best of both worlds of soft and hard suspension setups.
Other related articles from Bikeleague India
- Motorcycle chain – how to clean, adjust & maintain
- Motorcycle riding style – How to choose your perfect bike
- Two wheeler tyres – Different types, pros & cons
- Ducati Supersport 950 S
- Ducati Supersport 950
Conclusion
This guide has discussed different types of motorcycle suspension, their pros and cons, and some frequently asked questions related to two-wheeler suspension. If you have any other doubts or queries, email us at bikeleague2017@gmail.com. You can also share your doubts or opinions in the comments section below. We are always eager to help and assist you. Also, here are several social media platforms of Bikeleague India to raise your suspicions.